Amylase Liquid
Amylase Liquid Specification
- Bio-Degradability
- Yes
- Assay Method
- Spectrophotometric
- pH Range
- 5.5 - 7.0 (at 1% solution)
- Odor
- Characteristic
- Color
- Light Brown
- Form
- Liquid
- Application
- Textile, Food, Brewing, Paper, Detergent
- CAS Number
- 9000-90-2
- Enzyme Activity
- 40,000 U/ml (minimum)
- Shelf Life
- 12 months
- Stability
- Stable under recommended storage conditions
- Handling Precautions
- Use protective gloves and goggles when handling
- Purity
- 98%
- Solubility
- Completely soluble in water
- Storage
- Store in cool & dry place, avoid direct sunlight
- Moisture Content
- Less than 5%
- Product Name
- Amylase Liquid
- Pack Size
- 25 kg, 50 kg HDPE drums
Amylase Liquid Trade Information
- Minimum Order Quantity
- 100 Milliliters
- Sample Available
- Yes
- Sample Policy
- If order is confirmed we will reimburse the sample cost
- Main Domestic Market
- All India
About Amylase Liquid
Alpha-amylase hydrolyzes 1,4-glucosidic linkages in starch and other polysaccharides to form short chain oligosaccharides. The substrate used in reagent is 2-chloro-4-nitrophenyl-a-galactosylmaltoside (GALG2-CNP). The rate at which pnitrophenol is formed is directly proportional to the amylase activity in the sample. The resulting increase in absorbance can be measured spectrophotometrically at 405 nm.
High Purity for Superior Performance
Amylase Liquid features a purity level of 98%, ensuring optimal results in industrial and manufacturing processes. Its robust enzyme activity guarantees reliable starch breakdown, contributing to efficiency in applications ranging from food processing to textile production.
Safe Storage and Handling
Designed for longevity, Amylase Liquid should be stored in a cool, dry environment away from direct sunlight to maintain its 12-month shelf life. Wearing protective gloves and goggles during handling prevents contact and upholds safety standards in industrial settings.
Versatile Industrial Applications
This product is ideal for uses in textiles, brewing, food processing, detergent formulation, and paper manufacturing. Its characteristic odor and light brown color make it easy to identify, while complete water solubility allows effortless mixing and process integration.
FAQs of Amylase Liquid:
Q: How should Amylase Liquid be stored to maximize its shelf life?
A: Amylase Liquid should be kept in a cool, dry place and away from direct sunlight. Proper storage preserves enzyme activity and extends its shelf life to 12 months.Q: What protective equipment is recommended when handling Amylase Liquid?
A: When working with Amylase Liquid, it is essential to wear protective gloves and goggles to prevent direct skin or eye contact, ensuring safe handling practices.Q: When is Amylase Liquid used in industrial processes?
A: Amylase Liquid is commonly applied during starch hydrolysis stages in industries such as textile, food, brewing, paper, and detergent manufacturing to improve process efficiency and product quality.Q: Where is Amylase Liquid manufactured and exported from?
A: This product is manufactured, supplied, and exported by companies based in India, ensuring quality control and industry compliance.Q: What is the main benefit of using Amylase Liquid in manufacturing?
A: The primary advantage is its high enzyme activity and purity, which facilitate rapid and effective starch breakdown. This enhances productivity and quality in industrial operations.Q: How is the assay of Amylase Liquid determined?
A: Amylase Liquids assay is determined using the spectrophotometric method, which accurately measures enzyme activity concentration to ensure consistent product performance.Q: What is the process for using Amylase Liquid in applications?
A: To use Amylase Liquid, dilute it to the required concentration (typically in water) within its recommended pH range of 5.57.0, then incorporate it into process streams for starch modification or breakdown.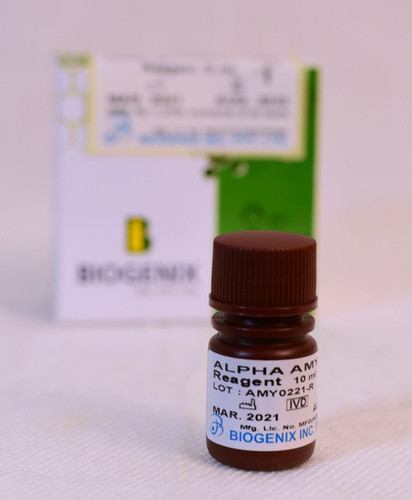
Tell us about your requirement

Price:
Quantity
Select Unit
- 50
- 100
- 200
- 250
- 500
- 1000+
Additional detail
Mobile number
Email


 Send Inquiry
Send Inquiry Send SMS
Send SMS
